The S&P 500, or Standard & Poor’s 500 Index, is a stock market index that measures the performance of 500 large companies listed on stock exchanges in the United States. It is widely regarded as one of the best representations of the U.S. equities market and a key indicator of the overall health of the economy. The index covers approximately 80% of the market value of all publicly traded stocks in the U.S. and includes companies from various sectors such as technology, finance, healthcare, and consumer goods.
Non-Farm Employment: A Key Economic Indicator
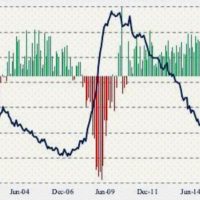
Non-Farm Employment (In Taiwan, it is called “非農就業“) is a crucial economic indicator that measures the number of paid workers in the United States, excluding the agricultural sector. It is released monthly by the Bureau of Labor Statistics and is considered one of the most important economic reports, as it directly impacts the U.S. dollar and financial markets. The NFP report is closely watched by investors, policymakers, and economists because it provides insights into the health of the U.S. labor market and the overall economy.
The Impact of Non-Farm Employment on the S&P 500
The relationship between Non-Farm Employment and the S&P 500 is significant because the performance of the U.S. labor market can influence investor sentiment and market expectations. When Non-Farm Employment numbers are strong, it indicates a growing economy, increased consumer spending, and higher corporate earnings, all of which can positively impact the S&P 500. Conversely, weak NFP numbers can lead to negative market reactions and decreased investor confidence.
Economic Growth and the S&P 500
Economic growth is a primary driver of stock market performance, and the S&P 500 (In Taiwan, it is called “標普500是什麼“) is no exception. As the U.S. economy expands, companies in the S&P 500 are likely to see increased revenues and profits, which can lead to higher stock prices and a stronger index. Non-Farm Employment is a key component of economic growth, as a robust labor market contributes to higher consumer spending and business investments. When more people are employed, they have more disposable income to spend, which in turn stimulates economic activity and supports the S&P 500.
Inflation and the S&P 500
Inflation is another critical factor that influences the performance of the S&P 500. High inflation can erode the purchasing power of consumers and lead to higher interest rates, which can negatively impact corporate earnings and stock prices. Non-Farm Employment can influence inflationary pressures, as a tight labor market with low unemployment can lead to wage growth and increased production costs. This can result in higher prices for goods and services, affecting the overall inflation rate and, by extension, the S&P 500.
Market Volatility and the S&P 500
Market volatility is an inherent aspect of investing, and the S&P 500 is not immune to fluctuations. Non-Farm Employment data can cause significant market movements, especially when the reported numbers deviate from market expectations. Unexpectedly high or low NFP figures can lead to increased volatility in the S&P 500, as investors react to the new information and adjust their portfolios accordingly. This can result in short-term price swings and increased uncertainty in the market.
Central Bank Policies and the S&P 500
Central bank policies, particularly those of the Federal Reserve, play a significant role in shaping the performance of the S&P 500. Monetary policy decisions, such as interest rate adjustments, can influence the cost of borrowing and the overall economic environment. Non-Farm Employment data is one of the key factors that the Federal Reserve considers when making these decisions. Strong NFP numbers can signal the need for tighter monetary policy to prevent overheating, while weak numbers may call for looser policies to stimulate growth. These policy changes can have a direct impact on the S&P 500 and its constituent companies.
Conclusion
In summary, the S&P 500 is a vital barometer of the U.S. stock market and the broader economy, and Non-Farm Employment is a critical economic indicator that influences its performance. The health of the U.S. labor market, as reflected in NFP data, can shape investor sentiment, economic growth, inflation, market volatility, and central bank policies, all of which have a direct bearing on the S&P 500. Understanding the relationship between Non-Farm Employment and the S&P 500 is essential for investors seeking to navigate the complexities of the financial markets.